PARKING LOT ISSUES AND CASES
Louisiana law is not written in favor of those people who trip and fall or slip in fall in parking lots. While the standard of care is slightly lower than a slip and fall or trip and fall inside of a retail store, it is still very difficult to prove/win these cases. I will outline what is the standard of care, what questions must be asked in every case and my overall impression of what every injured person must be aware of when making a decision to pursue legal action against the parking lot owner and/or manager.
Risk of Harm:
In determining whether the risk of harm is unreasonable, there are numerous factors. The two main factors are:
- The degree to which a danger may be observed by a potential victim. How easy is it to see?
- The number of falls previously caused by the “alleged” defective condition.
Questions to be asked if its believed to be a deviation from the normal surface
While many questions are very case specific, here are a few questions that I ask in all cases.
- Have falls been caused by this condition before? If so, how many and when?
- Was the ground wet or dry?
- Has my client been to this place before? If so, has my client walked past or over this “defect” before? Are they familiar with the parking lot and how so?
- Was the “defect” located in a walkway or in an area where it would be anticipated people would be or could be expected to walk?
- When the fall occurred, what was my client doing? Talking on the phone, distracted?
Louisiana Civil Code Article 2317.1 is our guide
Damages caused by “ruin, vice or defect” is fully described in this article. The law states that the owner or custodian of the property is responsible for damages that occur due to the “ruin, vice or defect” but only if we can show that the owner knew of the problem, or by “exercising reasonable care” that he should have known of the problem; AND that the problem could have been prevented or fixed by using reasonable care; AND that he failed to do so.
Is there a fixed rule or standard to determine an Unreasonable Risk of Harm
No. There is no standard as each case is different, each fall is different, and the specific facts are unique to each case. Therefore, a judge or jury must determine if the “thing” presents an unreasonable risk of harm. It will determine whether the social value and utility of the hazard outweigh and justify its potential harm to others.[1] So the judge or jury will determine if the alleged defect presents an unreasonable risk of harm based on those case specific facts.[2]
Irregularities in surfaces are common
It is common for streets, sidewalks, driveways, and parking lots to have deviations and not perfectly smooth surfaces – irregularities. Courts have recognized this and noted that it is not the duty of the owner of these locations to eliminate all variations in elevations along the cracks, seams, joints, and curbs. These surfaces are not required to be smooth and free from deviations because to require that would be impossible.[3] But the defendant landowner can’t rely on this “unreasonable analysis” alone.
Not every minor imperfection or irregularity in the “thing” or spot of the fall is a defect that gives rise to delictual responsibility. That irregularity or imperfection must be of such a nature as to constitute a dangerous condition which would reasonably be expected to cause injury to a regular person exercising ordinary or normal care, meaning a regular person behaving normally and walking normally in that particular situation.[4] The law only requires property owners to keep their property (premises) in a safe condition for use in a manner consistent with the purpose for which the property is intended to be used.[5] So you can see that is a general statement from the courts and now understand why each case is fact specific.
What makes it unreasonable
The answer is a mixture of facts and law. The judge or jury will ultimately determine if the area of the fall presented an unreasonable risk of harm. Many items are taken into consideration and because it requires a balancing of the risk and utility of the area, it is not a simple rule of law that can be applied to the facts of all cases. So the facts and circumstances of each case must be considered in making this determination.[6]
Does the size of the crack or deviation matter?
Yes it does! A crack of less than 1/8” wide and a height difference of ½” that caused a
person to fall and no known history of falls at that spot was noted, was found by the court to not be sufficient enough to make the landowner liable.[7]
Why would the courts and law support un-smooth parking lots in many cases? Many courts follow this – the cost to eliminate all such minor defects is too much; the cost to keep surfaces free from defects is impossible and cost prohibitive.[8]
Conclusion
So what does this all mean? Trip and fall cases are difficult to win. Courts have stated that each case must be evaluated on its own facts and circumstances. The law seems to favor the property owner. Is the spot where you fell one of those cost prohibitive acceptable defects referenced above? Have others fallen there and been injured? These are all questions that should be answered to know if you have a claim or not. I have handled trip and fall cases and would be honored to evaluate your situation.
[1] Reed v. Walmart Stores, Inc., 97-1174 (La. 3/4/98), 708 So.2d 362.
[2] Johnson v. Brookshire Grocery Co., Inc., 32,770 (La. App. 2d Cir. 3/1/00), 754 So.2d 346, writ denied, 00-0938 (La. 5/26/00), 762 So.2d 1107.
[3] Reed
[4] Deville v. State Farm Ins. Co., 617 So. 2d 1255 (La.App. 3 Cir. 1993).
[5] Kerry v. Basco, 96-289 (La.App. 3 Cir. 10/9/96); 687 So. 2d 420.
[6] Dupree v. City of New Orleans, 99-3651 (La. 8/31/00), 765 So.2d 1002; Waller v. Shelter Mut. Ins. Co., 41,215 (La. App. 2d Cir. 6/28/06), 935 So.2d 288.
[7] McGehee v. Seville Square Condominiums Homeowners Association, Sabrier, and Scottsdale Insurance Company, No. 2002 -CA – 719 (La. App. 1 Cir. 12/11/02), 836 So.2d 306
[8] Reed.
SLIP/TRIP AND FALLS IN LOUISIANA
Louisiana law does not favor the victim in these types of personal injury cases. A much heavier burden is placed on the injured person to prove that the landowner, merchant/store is at fault for injuries sustained. The statute is La. R.S. 9:2800.6 that applies to all trip and fall or slip and fall cases where the location of the fall is at or in a store. This is a “merchant liability statute.” While there are countless cases on the topic, Jones v. Brookshire Grocery Co., 37,117 (La. App. 2 Cir. 5/14/03), 847 So. 2d 43 is a good outline of the standards.
If a claim for premises liability (outside of a store) exists, applying La.C.C. Art 2315 (general negligence) or 2317.1 (premises liability), the same duty/risk analysis applies.
What duty does the merchant owe to its customers?
A merchant owes a duty of reasonable care to its customers or “the general public” who use or enter his premises. The merchant must exercise reasonable care to keep the aisles, passageways, and floors in a reasonably safe condition. This includes reasonable efforts to keep the premises free of any hazardous conditions that may cause damage or injury. And a landowner must discover any unreasonably dangerous conditions on the property; either correct/fix it or warn others of its presence. This seems kind of vague – reasonable care? Reasonable efforts? Each case is fact driven so we must look at the specific facts of each case.
What do you need to prove?
In a claim against a merchant by someone injured while legally on their property for damages because of a fall, death or other loss sustained due to a condition existing on the property, the injured person (claimant) has the burden of proving, in addition to all other elements of the cause of action, ALL of the following:
- The condition presented (created) an unreasonable risk of harm to the claimant AND that risk of harm was reasonably foreseeable.
- The merchant either (a) created or (b) had actual or (c) constructive knowledge/notice of the condition that caused the damage BEFORE the incident.
- The merchant failed to exercise reasonable care. One way to determine reasonable care is to determine whether a written or verbal uniform policy exists regarding cleanup or safety procedures is insufficient, alone, to prove failure to exercise reasonable care. Without a policy, the merchant would have a hard time explaining how they do so.
“Constructive notice” means that the condition existed for such a period of time that it would have/should have been discovered by a merchant who was using reasonable care. Just having an employee in that area may not be enough, you would have to show that the employee knew or should have known of the hazard – was reasonable care used.
Failing to prove any of these 3 will end the claim.[1] White also states that in addition to proving these 3 points, a plaintiff must present evidence that the hazardous condition existed for such a time that it would be sufficient to place the merchant on notice of the condition. This is called the “temporal” element.[2] There is no set amount of time to pass, but the plaintiff must show it existed for long enough or “such a time period.”[3]
You also need to show that the “thing” complained of was in the defendant’s custody. So the “thing” contained a defect that presented an unreasonable risk of harm and that this defective condition caused the damages; and, the defendant knew or should’ve known of the defect.[4]
What does the merchant have to prove?
The merchant/store-owner has a duty of care to take reasonable protective measures, including periodic inspections of the property to ensure that it is kept free from hazards like substances on the floor or conditions that may cause a customer to fall.[5] Determining “reasonable measures” is done on a case-by-case basis, as discussed in the Hardman and Ward cases. So you look at the risks involved, the overall volume of business, time of day, section of store, type of business, etc. and the degree of vigilance must match those factors.
Determining “Unreasonably Dangerous”
While we are each entitled to our own opinions, in personal injury cases, in addition to our client’s opinions, we must look at how courts determine. Courts use a risk-utility balancing test that includes these components:
- The use or utility of the thing complained of;
- The likelihood and magnitude of harm – including the obviousness and a noticeability of the thing;
- The costs of preventing the harm – can it be fixed or removed?
- The nature of the plaintiff’s activities at the time of the fall/injury – were they dangerous by nature?[6]
Open and Obvious:
Generally, a defendant has no duty to protect against “open and obvious” hazards. So if the facts show the hazard should be obvious to everyone, then the condition may not be unreasonable and the defendant may owe no duty to the plaintiff.[7] So the trip and fall duty is not just on the landowner, the pedestrian has a duty to see what should be seen and to determine if their pathway is clear.[8] One factor to determine if the condition is unreasonably dangerous is if it may be observed by a potential victim – making it possible that even though you fell, if the condition is deemed to be open and obvious (other people would have seen it using “reasonable care”) then the landowner may not be liable.[9] The hazard should be open and obvious to everyone who may potentially encounter it.[10] But recently, the Louisiana Supreme Court stated that “open and obvious” is not stated in any of the premises liability statutes and is a “figment of judicial imagination.”[11]
The more obvious the risk, the less likely it would be to cause injury because it would be avoided. So location matters. Was the hazard in a commonly traversed area? Was it in an area not well trafficked? I need to know was the hazard in an area where other visitors or shoppers would likely encounter it or in an area where they would be “forced” to go?
The Louisiana Supreme Court clarified where open and obvious is within the breach of duty element of the duty/risk analysis and is not a jurisprudential doctrine barring recovery, but only a factor of the risk/utility balancing test – considering the likelihood and magnitude of harm, and it’s not a consideration for determining the legal question of the existence of a duty. So it is improper to state that a defendant generally does not have a duty to protect against the open and obvious. With limited exception, there is the duty to exercise reasonable care and to keep the property free from unreasonable risks of harm. The breach of the duty element is a mixed question of law and fact.[12]
Conclusion:
Proving a slip and fall and trip and fall case in Louisiana can be very difficult. Each case is fact intensive and must be properly evaluated. Documentation is key in such cases. When possible, taking photos at the scene are extremely important because it is common that a store/merchant does not have cameras showing that area or “the camera there is broken.”
[1] White v. Wal–Mart Stores, Inc., 97–0393 (La.9/9/97), 699 So.2d 1081; Alexander v. Wal–Mart Stores, Inc., 96–1598 (La.App. 3d Cir.2/4/98), 707 So.2d 1292, writ denied, 98–0572 (La.4/24/98), 717 So.2d 1169.
[2] Turner v. Brookshire Grocery Company, 34,562 (La.App.2d Cir.4/4/01), 785 So.2d 161, citing Rodgers v. Food Lion, Inc., 32,856 (La.App.2d Cir.4/5/00), 756 So.2d 624, writ denied, 00–1268 (La.6/16/00), 765 So.2d 339; Davis v. Wal–Mart Stores, Inc., 31,542 (La.App.2d Cir.1/22/99), 726 So.2d 1101.
[3] Kennedy v. Wal–Mart Stores, Inc., 98–1939 (La.4/13/99), 733 So.2d 1188.
[4] Taylor v. Chipotle Mexican Grill, Inc., 18-238 (La. App. 5 Cir. 12/27/18), 263 So.3d 910, 914.
[5] Hardman v. The Kroger Company, 34,250 (La.App.2d Cir.12/6/00), 775 So.2d 1093; Ward, supra; Stevens v. Winn Dixie of Louisiana, 95–0435 (La.App. 1st Cir.11/9/95), 664 So.2d 1207.
[6] Bufkin v. Felipe’s Louisiana, LLC, 14-288 (La. 10/15/14), 171 So.3d 851, 856; Broussard v. State ex re. Office of State Buildings, 12-1238 (La. 4/5/13), 113 So.3d 175, 184.
[7] Pitre v. La. Tech Univ., 95–1466, 95–1487 (La.5/10/96), 673 So.2d 585, 591.
[8] Hutchinson v. Knights of Columbus, Council No. 5747, 2003–1533 (La.2/20/04), 866 So.2d 228, 235
[9] Id.
[10] Broussard, 113 So.3d at 184; Caserta v. Wal-Mart Stores, Inc., 12-853 (La. 6/22/12), 90 So.3d 1042, 1043 (per curiam); Hutchinson 5747, 03-1533 (La. 2/20/04), 866 So.2d 228, 234.
[11] Farrell v. Circle K Stores, Inc., 2022-00849 (La. 3/17/23), 359 So. 3d 467, 475.
[12] Id.
Types of Auto Insurance Coverage Available to You
Let’s face it, insurance is not cheap. Insurance is something you hope you never need, but when you do, you need it. Auto insurance is no different that any other type of insurance – it costs more than you would like to pay and it can be complicated to understand. Calling around to find who has the cheapest rates is not the best method and you may be guilty of having done this before but read on to understand the importance of auto insurance and the different “add-ons” you should purchase and why purchasing from a company that has a strong presence in the state and has been in business for many years is important.
Where to and how to shop for coverage
You should only purchase from authorized insurance companies and produces in the state. Those who are not may be a scam, unauthorized companies are illegal in Louisiana and if the company goes broke, you may have no coverage. Speaking with friends and family is a great place to start, word of mouth. Also look online. Go to, https://www.ldi.la.gov/home to research companies to determine if they are: legitimate, authorized by the state, and if the company has any red flags that the Department of Insurance may warn the public about.
“Full Coverage” is a Joke – Liability Only
“I have full coverage” has a good ring to it, but most people have no idea that “full coverage” is really the Louisiana minimum auto insurance coverage required by law. The minimum auto insurance coverage in Louisiana is liability coverage only, meaning you are only purchasing coverage to protect you if you injure someone else or cause damage to their property. Those limits are known as 15/30/25 – a limit of $15,000 per person injured, not to exceed a total payment of $30,000 to all those injured, and $25,000 for property damage. So, if you only have the minimum limits, then you have nothing protecting you if you are injured or your vehicle if it is damaged.
This liability only coverage will also extend coverage to any licensed driver you give permission to use your vehicle. It also applies when you are driving rental cars or another person’s vehicle, when you have their permission.
“Add-on:” Medical Payment Coverage
This is an inexpensive add-on to the minimum limits coverage and is the first step in protecting you if you are injured, no matter who is to blame. This feature will pay for medical expenses (ambulance, ER, doctors, etc.) up to the policy dollar limits you have purchased. It will also help with funeral expenses. This coverage applies to you and anyone in your vehicle.
“Add-on:” Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage:
This is coverage that can protect you, your occupants, and your vehicle. But this is a tricky area of coverage because there are different types of UM. Generally, UM or UIM coverage will pay benefits to you if you are involved in a crash with an at fault driver who has no insurance or not enough insurance, as well as any occupants in your vehicle. This will include medical bills, lost wages, property damage, and general damages (pain and suffering). It also provides coverage in a hit and run crash.
“Add-on:”Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Economic Only Coverage:
This coverage is similar to UM/UIM coverage, but has one major difference and for this reason, we do not recommend it. This “add-on” does not include coverage for compensation of your pain and suffering, loss of enjoyment of life, depression, anxiety, stress, etc. – what is called “general damages” and something we believe to be the most significant type of injury someone can suffer. It is available. We do not recommend it, but it is a few dollars cheaper than full UM/UIM coverage.
“Add-on:” Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Property Damage Coverage:
As the name implies, this “add-on” will provide property damage coverage if you are involved in a crash with an uninsured or underinsured driver. A deductible will exist and similar to liability coverage, there are limits that your coverage can be limited to, such as $25,000 or $50,000. You can purchase a higher level of coverage. But keep in mind that if you have collision coverage, this coverage may not be available.
“Add-on:” Towing and Rental:
As the name implies, this “add-on” will cover towing charges, including storage, and rental if you are involved in a crash. The rental coverage will have a daily limit for how much will be covered for a temporary replacement vehicle and a max length of days that would be covered.
“Add-on:” Comprehensive Coverage:
Comprehensive coverage pays for damage to your vehicle from situations like falling trees or branches, flood, fire, vandalism, theft, or a variety of named events specific to each policy. This would cover damages that are not a result of a vehicle crash. This coverage also has a deductible.
“Add-on:” Collision Coverage:
Collision covers just what you think, collision damage when you are involved in a crash with another vehicle. It does not matter who would be at fault. This coverage also has a deductible.
As a side note, do not think that because your car is older or not worth much that you should drop comprehensive and collision coverage. Many people believe that it is something that is not needed. But think about this, vehicle repairs are expensive, and crashes happen daily. Do you want to take the chance that if your car is damaged that you will be able to afford to repair it properly? Think of all the cars we see driving around with damage that the owner simply has not fixed. What do you believe the resale value looks like. Insurance for your vehicle is to protect your property and often time vehicles are the most expensive thing a person owns. Think twice about not purchasing or dropping this coverage.
Risks of Driving Without Auto Insurance:
Driving without insurance is illegal and irresponsible. Louisiana law requires all vehicle owners to maintain liability insurance coverage. That is the MINIMUM coverage. If you stopped and do not have valid insurance, you may receive a fine of up to $1,000 if you are knowingly driving without insurance and lying about having coverage. Simply not having proof of insurance or letting your policy lapse may also result in penalties. It is possible to have your license suspended and your car impounded.
If you are involved in a crash and do not have insurance coverage, you will suffer further losses but not being able to recover the first $15,000 of your claim’s value and $25,000 of your vehicle’s damages. This is commonly referred to as “No Pay, No Play” and it does not matter who is at fault.
Motorcycles
Let’s face it, many, if not most people, do not like motorcycles and, in particular, motorcycle riders. Some of the reasons we have heard is because riders break the law, cut in an out of traffic, ride between traffic, do “wheelies”, and speed off when a traffic light turns green. But most who ride motorcycles are responsible, law-abiding riders and many are business and professional people who ride for pleasure, relaxation, and a sense of freedom. Riding in heavy traffic and on busy roads is potentially very dangerous because riders have no protection if any type of vehicle crashes into them. So, we must ask what motorcycle riders must do to be responsible riders. The answers are simpler than one may think.
Is Motorcycle Riding Dangerous
Motorcyclists are more vulnerable to injury than a driver of a larger vehicle if involved in a crash. Research shows that over two-thirds of car/motorcycle collisions are the result of the other driver turning in front of a motorcyclist. Motorcyclists and cars/trucks need to mix in traffic without causing harm to each other. Motorcycles present a narrow silhouette and are usually much shorter in length than an automobile. The small profile of the motorcycle may make it appear farther away and traveling slower than it actually is. Remember that motorcycles are often hidden in a vehicle’s blind spot or missed in a quick look due to their smaller size. Because it is difficult to judge the motorcycle’s distance and speed, vehicle drivers need to take a second look, and then a third. Its small size also makes it more difficult to spot in traffic than another car. Some motorcyclists take advantage of their small size and maneuverability.
Not all motorcycles are the same. There is a broad range of motorcycles on the market, ranging from off-road to street motorcycles.
How to Make Motorcyclists Safe For Themselves and Motorists
The answers are quite simple:
- Obey all of our traffic safety laws, which apply to all vehicles and motorcycles alike.
- Perform regular motorcycle maintenance.
- Take motorcycle driver safety education classes.
- Wear proper safety clothing: boots that cover the ankles, leather or similarly protective pants and jackets, gloves, and a DOT-approved motorcycle helmet. Not all helmets are alike. The general rule is, if the person drops or damages his/her helmet, replace it before riding again. Don’t wear flip-flops, short pants, and short-sleeve shirts.
- Remember that motorcycles have a low profile and are hard for motorists to see. Assume that the motorists do not see you.
- Be mindful of the weather. Wet roads are slippery, especially when it first begins to rain because the rain has not yet removed the oil and slippery road residue.
- Have your rain gear available.
- Use turn signals or, alternatively, use hand signals when making left and right turns.
- Don’t tailgate.
- Know your motorcycle skill level and experience. Do not ride beyond your ability to ride safely. Not every rider has the same training, experience, and skills.
- Ride in the center of a travel lane, not off to one side or the other.
- Have a State driver’s license motorcycle endorsement.
- Know your motorcycle and its capabilities.
You May Need A Lawyer To Recover Your Damages
Under Louisiana law, a crash victim has one year from the date of injury to file a lawsuit or, if possible, settle the case. When this one-year period expires, the crash victim loses the right to sue the wrongdoer for both economic and non-economic damages.
Most people have no experience with the legal system and dealing with insurance companies. It is important to know that there are two Points of View (POV). The crash victim wants Justice, meaning full compensation. The insurance company wants to pay as little as possible for the injured person’s damages. The community in general POV about motorcycles and their riders is that they are “dangerous, killing machines.” So, if you need an attorney, you want one who cares about you, who spends time getting to know you, who keeps you informed about your case, who spends the necessary time to explain the law, and who knows what evidence is needed to prove all of your damages.
At the Law Offices of Richard R. Kennedy, you will have Richard Kennedy and Richard Kennedy III to represent you. Is this important? You bet? Why? First, together we have nearly forty years of riding motorcycles in many parts of the United States, from flat lands to mountains. Because you will know who is representing you; you know that we will keep you timely informed about your case and all the information you need for us to do our very best to get justice for you. When you call us, we answer your calls and we promptly answer your emails. The bottom line is simple: we and our clients get to know each other on a personal — not just a professional — level. That is critical in building trust. So, if you need a lawyer who is well versed in personal injury and has ridden motorcycles for over 30 years, call us.
Reduced Visibility Increases Risks of Crashes
Navigating Reduced Visibility: Safe Driving
Practices for Challenging Conditions
Driving is a responsibility that requires vigilance, attentiveness, and a keen sense of awareness. When faced with reduced visibility situations, the stakes are even higher. Reduced visibility, caused by factors such as fog, rain, snow, bright sunlight, or even darkness, significantly increases the likelihood of crashes and poses a serious threat to road safety.
What is a Reduced Visibility Situation?
A reduced visibility situation is one where your ability to see and be seen is compromised. These situations can arise due to various weather conditions and environmental factors. Common examples are :
- Fog: Fog can significantly impair your vision, reducing your ability to see the road, other vehicles, and obstacles. It can be particularly dangerous if it rolls in suddenly or is patchy.
- Rain: Rain can create a curtain of water on the windshield, making it challenging to see the road and other vehicles. Heavy downpours can also lead to hydroplaning, where your vehicle loses traction on the wet road surface.
- Snow and Ice: Snow and ice can blanket the road, making it slippery and affecting your control over the vehicle. Reduced visibility can also be caused by blowing snow or sleet.
- Darkness: Nighttime driving inherently reduces visibility. Reduced street lighting in some areas and glare from oncoming headlights can further complicate the situation.
So what should you do when encountering a reduced visibility situation? Some safe driving practices in reduced visibility situations include:
- Slow Down: Reducing your speed is one of the most effective ways to ensure safety in reduced visibility conditions. Slower speeds provide more time to react to unexpected obstacles.
- Increase Following Distance: Keep a safe following distance between you and the vehicle in front. In adverse conditions, the typical three-second rule should be extended to at least six seconds. This extra space allows you more time to react and stop if necessary.
- Use Your Headlights: Turn on your headlights, even during the day, to increase your visibility to other drivers. When in doubt, use your low beams rather than high beams, which can create glare in fog or rain.
- Keep Windows Clear: Make sure all your windows are clean and clear. Use defrosters and windshield wipers as needed to maintain good visibility.
- Use Fog Lights When Appropriate: If your vehicle has fog lights, use them only when visibility is significantly reduced, such as in dense fog or heavy snow.
- Avoid Distractions: In challenging conditions, your full attention should be on the road. Avoid using your phone, eating, or any other distractions that can divert your focus.
- Stay in Your Lane: Follow the lane markings and stay within your lane. Reduced visibility can make it easy to drift out of your lane, so stay attentive.
- Be Cautious at Intersections: Approach intersections with extra caution. Other drivers might not be as visible as they should be, and some may not adhere to traffic rules. Do not assume the other drivers are slowing to a stop or that they even can see the intersection controls.
- Plan Ahead: Before embarking on your journey, check weather forecasts and traffic reports. If conditions are particularly bad/adverse, consider delaying your trip or taking an alternative route.
- Know When to Pull Over: In extreme conditions, when visibility is almost nonexistent, it may be best to pull over to a safe location and wait for conditions to improve.
Conclusion
Reduced visibility situations are a challenging aspect of driving, but with the right practices, you can significantly reduce the risks. Prioritize safety, adapt to the conditions, and always be prepared for the unexpected. By following these safe driving practices, you can protect yourself, your passengers, and others on the road, making our highways safer for everyone, even in the most adverse conditions.

Basic Overview of Louisiana Insurance Law
BASIC LOUISIANA INSURANCE LAW
Car wrecks happen daily:
Vehicular wrecks happen daily, frequently causing serious injuries, death, and property damages. So it’s important to know some basics facts about Louisiana insurance law to know what insurance coverage is legally required and what additional coverages you should consider buying to protect yourself. A reputable insurance agent can help advise you about what coverages and policy limits will best protect you and your family. Honestly, Louisiana insurance law is vast and complex and, as such, this blog only discusses some of the more common auto insurance questions. Insurance liability requirements:
In Louisiana for a single wreck, you need $15,000 in bodily injury liability insurance per person ($30,000 per accident) plus $25,000 in property damage liability insurance to drive legally. These liability insurance requirements can also be written as 15/30/25. Liability insurance does not pay all of your damages. Liability car insurance comes in two forms: bodily injury liability coverage and property damage liability coverage. Bodily injury liability insurance covers expenses related to other parties’ physical injuries caused by your vehicle. Property damage liability insurance pays for repairs to the victim’s damaged property, including a car or a house.Louisiana’s “No-Pay, No-Play” Law:
Under Louisiana’s “no pay, no play” law, an owner or operator of a motor vehicle that is involved in an accident who fails to own or maintain compulsory motor vehicle liability security is prohibited from recovering his or her first $10,000 of bodily injury and his or her first $10,000 of property damage based on any cause or right of action arising out of the motor vehicle accident.
There are some exceptions to Louisiana’s “No-Pay, No-Play” law like, for example:
• It does not apply if you have the required minimum liability insurance.
• It does not apply to legally parked vehicles.
• It does not apply to drivers from another state if their state law does not require them to have liability insurance at the time of the wreck.
• It does not apply if the other driver is convicted of driving while intoxicated, intentionally caused the wreck, fled the scene, or acted in further the commission of a felony when the wreck happened.Comprehensive, Collision, and Uninsured Motorist Coverages:
When you are at fault in an accident, liability insurance coverage does not pay for any damage to your own property. It does not pay your medical bills, either. Liability coverage is not the only type of insurance you should consider. To be fully protected in the event of a wreck, you will need collision coverage, comprehensive, and uninsured motorist (UM) coverages. Statistics show that about one-third of Louisiana drivers have no liability insurance. And many, if not most, carry only the minimum liability insurance limits. Remember, UM coverage protects you and, if the other driver has no insurance or minimum liability insurance and your damages exceed the other driver’s policy limits, you will need your UM insurance to pay or help pay for all of your damages.Does the policy follow the owner or the vehicle:
Speaking generally, a car insurance policy in Louisiana usually follows the car. But you must check your policy’s exclusions — check for things like “insured vehicle” and “replacement vehicle” — to see if your policy provides that the policy follows the car or the insured as, for example, when the insured is driving someone else’s car. The bottom line is you must verify if your liability insurance policy follows you when you are driving a non-owned vehicle (one that you do not own) or if your policy follows your vehicle. Here you need to speak with your insurance agent, company, or an attorney.Comparative fault:
Louisiana has adopted what is known as a pure comparative fault scheme. When both drivers have insurance, the injured party (the plaintiff) only can recover the damages in the amount proportionate the defendant driver’s fault. As an example, if the plaintiff was 10% at fault, he or she can recover only 90% of his or her damages. The question of comparative fault is a fact question that the jury determines based on the evidence.Conclusion:
Louisiana insurance law is broad, vast, and complicated. When you are involved in a wreck, you should promptly notify your insurer or its agent or broker. Check your policy to see how much time you have to notify your insurer, which is normally 30 days. At the Law Offices of Richard R. Kennedy, we will fight to recover your full damages. The insurance company is not your friend. You want justice. The insurer just wants a quick settlement for less than justice requires. Contact us if you are injured or your vehicle is damaged in a wreck. We will review your case and advise you of your rights and what action is needed for you to receive justice. Feel free to contact us for a free consultation at (337) 232-1934 or at 1-800-440-1934. General Reminders for Interstate Driving
INTERSTATE DRIVING
Driving on the interstate can be intimidating, especially if you are a new driver or one who rarely travels on interstate highways. Generally, traffic on an interstate moves safely and smoothly. But when crashes do happen, they can be serious. So as a driver, let the following be a reminder of some basic safety rules and tips to follow to make your drive as safe as possible.
Plan ahead. Review your route and program in your destination into your mapping program or app of choice before you start. If you are taking a long drive, familiarize yourself with possible stops for food and gas along the way. Also, make sure that your car is in good condition for a long journey. Remember to not drive tired, so plan ahead.
Entering the highway can be done smoothly and safely. Make sure you bring your car up to speed in the on ramp or acceleration lane so that it matches the speed of traffic on the interstate. It is not proper to stop and wait for an opening, unless it is absolutely necessary. Begin checking traffic while you are on the entrance ramp. Use your signal and merge into the right lane of traffic in the available openings. As you merge, make sure you are traveling the same speed as interstate traffic. Continue driving at a steady speed and follow the speed limit. Remember that interstate traffic has the right of way and do not reply on other drivers to see you moving into their lane or that they will “give you space” to enter. Do not squeeze in, make sure you have a good cushion between the car behind you and the one in front.
Driving in the right hand lane. This is where you should be unless you are passing or exiting off of the interstate. If the roadway has more than two lanes in each direction, you can use the middle lane as a travel lane as well. Using the right lane as a place to begin slowing down for an exit ramp is dangerous, wait for the exit ramp to begin slowing down. Also, when you are approaching an exit ramp, stay alert for those drivers who may swerve in front of you because they are not paying attention and fearful of missing their exit.
Keep a space/distance cushion and don’t tailgate. Rear-end collisions are the most frequent type of crashes on the interstate. By keeping a cushion of space around you (in the front, to the sides, and in the rear) you have time, distance, and space to avoid hazards and mistakes other drivers may make. By checking your mirrors you will notice if other vehicles are crowding you or tailgating you. If you are being crowded, it is because of an unsafe driver who is not attentive as you. Safety experts tell us that if you are being tailgated, slow down and, if possible, move to the outside lane and allow the unsafe driver to pass you. Avoid driving along side other cars, stay in the middle of your lane and making room for others merging onto the interstate are all great tips.
Maintaining your space cushion is accomplished by maintaining your lane position, adjusting your speed to match the flow of traffic and by using your signals (communicating with other drivers) when you intend to leave your lane of travel and enter another lane.
Exiting the interstate is not always as easy as you may think. Proper planning with make you aware of where and when you need to exit. Knowing your route, using your map apps and paying attention to the exit signs will let you know how far until your exit, if you need to change lanes to exit, and exactly where to exit. On the interstate, use your blinker for 5 seconds before changing lanes and if you have to move more than one lane to get to your exit, just move one lane at a time. Be sure to adjust your speed for the exit ramp to so you will safely exit the interstate. If you miss your exit, DO NOT STOP or BACKUP!!! Simply continue driving and exit at the next exit to turn around.
If you have been involved in a crash on the interstate, or even in town, do not wait to contact us. The sooner you call, the sooner we can begin to evaluate your case and begin helping you. Louisiana law requires that you take legal action within 1 year of the date of the crash or you give up your right to recover.
GENERAL AND SPECIAL DAMAGES
Louisiana law provides a person who injures or damages another person must pay the injured person’s damages. The injured person (plaintiff) must prove his or her damages by a preponderance of the evidence. This simply means that the wrongdoer’s act or inaction more probably than not injured the plaintiff. In a criminal case, the penalty is jail or death. But in a civil case, the remedy is money damages.
The civil law provides for compensatory damages (money), which includes general and special damages. In certain limited situations, the law provides for punitive damages.
General damages are speculative and cannot be fixed with mathematical certainty. Your body produces no receipt for how it has suffered. So, jurors must consider all the evidence dealing with pain and suffering. And they need to use their common sense to arrive at a just verdict. These damage include:
- physical pain and suffering;
- mental anguish, anxiety, and distress;
- inconvenience;
- loss of intellectual gratification of physical enjoyment;
- permanent or temporary disability and loss of physical functions of the body;
- past and future loss of the enjoyment of life;
- any other factors that affect the victim’s life that cannot be definitely measured in terms of money.
Unlike general damages, special damages are meant to restore plaintiffs to the financial position they would have been in if they had not been wrongly injured. These damages can be fixed with mathematical certainty and include the following:
- past medical bills,
- estimated future medical expenses,
- past wage or economic losses,
- future loss or reduction of wage losses,
- loss of company or employment benefits,
- damages to the plaintiff’s property.
In summary, general damages address intangible losses like pain and suffering, while special damages cover concrete, measurable financial losses. We spend a great deal of time getting to know our clients and to best understand how their injuries have impacted their lives, putting us in the best position to properly explain to a judge and jury the nature and extent of our client’s general damages through stories and examples.
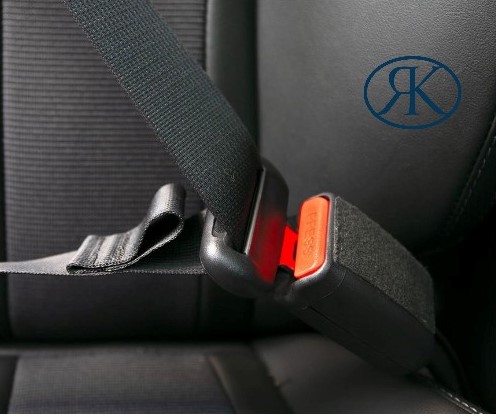

Doing this one thing may save your life while in a car
FALSE ASSUMPTIONS ABOUT MOTOR VEHICLE CRASHES AND WHY SEATBELTS ARE IMPORTANT
Many people, if not almost all, believe most crashes that result in deaths happen at high speeds and well away from our homes. Wrong. The facts do not support these assumptions or beliefs. Rather, the data shows that 80% of deaths occur in cars traveling less than 40 miles per hour, and 75% of crashes occur within 25 miles of our homes.
Louisiana law makes it mandatory for all drivers and passengers in cars, vans, and pickup trucks to wear seatbelts. Wearing a seatbelt reduces the risk of serious injury and death by 50%. Those less likely to wear them are teens, commercial drivers, males in rural areas, pickup drivers, people driving at night, and people who have been drinking. The bottom line is simple. “Buckle up.” Studies show that wearing a seatbelt is the smartest move that drivers can make to prevent injury or death. Here are some facts:
- Your chances of being killed are 25 times greater if you are thrown from your vehicle.
- Non-belted fatalities have been recorded at speeds as low as 12 miles per hour.
- The force of an impact at just 10 miles per hour is equal to the force of a 200 pound bag of cement dropped from a first story window.
- If everyone who is involved in a crash wore a seatbelt at the time of the crash, 60% more lives could be saved.
- 1 in 7 adults choose not to wear seatbelts.
Concerning children, the Louisiana Child Passenger Restraint law requires that all children must be properly restrained and secured in an age- or size-appropriate passenger restraint system that meets the applicable federal motor vehicle safety standards. Here is that information:
- A child 6 years or younger or under 60 lbs. may not be transported in the front seat of a vehicle with an active airbag.
- Birth or less than 20 lbs. at any age – rear-facing, federally approved car seat
- 1-4 years, at least 20 lbs. but less than 40 lbs. – forward-facing, federally approved car seat
- 4-6 years, at least 40 lbs. but less than 60 lbs. – booster seat with restraints
- 6 years, more than 60 lbs. – booster seat with restraints or seat belts
- Booster seats are an appropriate option for a child of any age.
If you remember one thing it is wearing seatbelts saves lives and reduces the risk of serious injuries. To repeat, “Buckle up” and make sure that your passengers and children also are buckled up and in proper restraints.
If you have been injured in a crash and have questions, call us today! The sooner we meet, the faster we can evaluate your case and, if you choose to hire us, the faster we can begin to help you maximize your recovery.

Don’t Get Turned Around in A Roundabout
Roundabouts are also called traffic circles. Roundabouts are one-way, circular intersections designed to improve safety and efficiency for motorists, bicyclists, and pedestrians. In a roundabout, traffic flows counterclockwise around a center island. A roundabout redirects some of the conflicting traffic, such as left turns, which cause crashes at traditional intersections. This is because drivers enter and exit the roundabout through a series of right-hand turns.
Roundabouts replace regular intersections. They do not have stop signs, which eliminates the cost of electric traffic signals. Drivers must yield when entering and exiting a roundabout and must travel in a counterclockwise direction. Greater safety is achieved primarily by slower speeds and the elimination of more severe crashes and operation is improved by smooth-flowing traffic with less stop-and-go than a signalized intersection. Aesthetics are enhanced by the opportunity for more landscaping and less pavement, according to the DOTD. Roundabouts were first introduced in the U.S. in the 1990s. And since September 2003, some 174 more have been built in Louisiana according to the DOTD.
While intended to improve traffic flows and increase safety, roundabouts do not eliminate all traffic crashes. Many of the roundabout crashes are caused by drivers who are unfamiliar with them and the traffic rules that govern them. It is important to know that roundabouts may have two or more lanes, so know which lane you need before you enter the traffic circle.
Common Reasons for Crashes At Roundabouts
- Failure to yield to traffic that is already in the circle.
- Failure to yield to bicyclists and pedestrians.
- Drivers who stop abruptly in the circle because they are confused or missed their turn.
- Speeding when entering the circle.
Preventing Roundabouts Crashes
You cannot control the actions of other drivers. But if you obey some basic rules for roundabouts, you can help prevent a wreck:
- Slow down as you approach a roundabout.
- Yield to traffic that is already in the roundabout.
- Use your turn signal when exiting the roundabout.
- Give trucks and larger vehicles enough space to maneuver and exit the roundabout.
- Do not stop once you are in the traffic circle.
- Know which exit you need to take before you enter the circle.
Roundabout Crash Legal Timeline
Under Louisiana law, an crash victim has one year from the date of injury to file a lawsuit or, if possible, settle the case. When this one-year period expires, the crash victim loses the right to sue the wrongdoer for both economic and non-economic damages.
If You Need An Experienced Attorney
Call us today. We have been helping those injured for over 50 years. We work for our clients, explaining the laws that protect them, the laws that were broken, understanding the facts and our client’s injuries and how those injuries have impacted their daily lives, their goals, and their dreams. So, if you need a great lawyer, call us at (337) 232-1934 to get started.